سایت آموزش پیوند درختان ( www.LinkTrees.ir) مقالات کشاورزی و باغبانی : Grafting Grape Vines
Grafting Grape Vines
Grafting is a process by which two grape vine plants are combined to create an improved single vine with new desired attributes. Grape vines can also be grafted to either convert a vineyard to a grape variety that is anticipated to receive high premiums, or to remove a grape variety for which there is little to no market demand
The two most common grafts for grape vines are combining a local bareroot with a new variety of grape vine, and combining a new vine with an old vine’s established trunk. For the greatest success grafting occurs during the dormant winter season – grafting techniques include; Omega, Whip, Chip bud, T-bud, Cleft, Notch and Bark grafting (image below). Grafting in the vineyard can take several months to complete
Grafting or budding is an asexual propagation technique. This is the process of placing a shoot system (a scion) of one cultivar or species on the root system (a rootstock) of another. When grafting, the scion will contain multiple buds, but budding consists of a single bud. The only requirement for grafting and budding is viable cambium contact. The cambium is a single layer of cells located just below the bark. This area leads to the formation of the graft union of the scion and rootstock. It is subject to drying out, so take steps to prevent that situation. Increased cambial contact (the more area that touches) between scion and rootstock increases the chances of success
Successful Grafting
Grafting is a time-consuming process requiring patience and practice. Already existing vines are candidates for grafting if the cultivar is not economical or not appropriate for the site. The vines to be grafted must be healthy and vigorous, without disease or insects, and relatively young. Scion wood collection is the same as for taking cuttings. The scion is taken while dormant for most types of grafting; however, actively growing tissue can be used in some cases. There are several types of grafts that can be used, including
Cleft grafts
Bark grafts
Whip grafts
Budded grafts
Green growing bench grafts
The cleft grafting technique
The cleft graft is a simple method that requires little skill. It is for larger diameter vines and the scion must be dormant. There is a five step process for the cleft graft
Cut off the top of the vine about 30 minutes or so before grafting
Split the rootstock with a blade or chisel
Hold the split open and prepare the scions by cutting one end to a “v” shap
Place one scion on each side to fit with the cambium
Tape the split area together and use grafting compound to seal the splits to keep excess moisture out and seal moisture in
The bark graft is also relatively easy and requires little skill to make it successful. The bark must be “slipping” for this graft to work, so timing can vary from rootstock to rootstock. The scion must be dormant. The bark grafting process is
Select the vine and cut off the top
Prepare the scion by cutting a pattern into the basal end
Make matching pattern cuts on the rootstock
Insert scion and secure it to the rootstock with a grafting band or tape
Cover the area and seal the cut with grafting wax
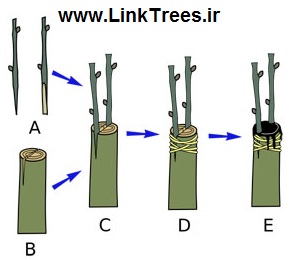
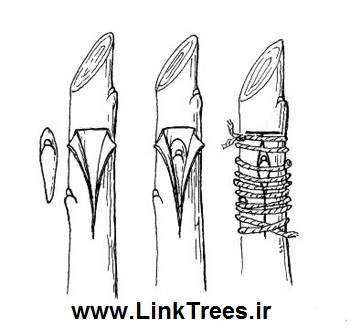
Whip grafting is a common way to propagate many different plants. For the rootstock, use 1- to 2-year old vines, up to 3/4-inch in diameter. The scion size should match with the size of the rootstock. This type of graft can be done in the field or in the greenhouse. The process of whip grafting is:
Cut the scion at an angle about 1 to 2 inches long
Cut the rootstock at an angle at the same length
Match up the cambiums
Cut a tongue in both the scion and the rootstock
Wrap the graft and seal it
Budding
Budding is somewhat different from grafting in that only one bud is used. Budding has many variations, but T-budding (also called shield budding) is commonly used in fruit species. Buds for T-budding must be mature and dormant, taken from healthy and vigorous wood
Remove the leaf blade, leaving only the petiole intact, which acts as a handle
Shave the bud off the budwood. You only need a small sliver of wood
On the rootstock, make a vertical cut to separate the bark from the cambium, then make a perpendicular cut at the top of the vertical cut to form a “T.”
Carefully peel back the bark to expose the pocket for the bud shield
Slide the bud shield into the open pocket and trim off the top if needed
Wrap tightly with grafting tape, but leave the bud exposed
After the healing process starts and you observe growth, you can remove the rootstock that was left above the budded area
There is a rapid graft propagation technique where the callused graft is rooted under mist for 30 days, grown in a greenhouse for 30 days, conditioned in a lath house for 30 days and planted in the vineyard in mid to late spring (May, in northern areas). Vines from this system are called green growing bench grafts. Summer temperatures, sunlight, and low humidity can make green growing bench grafts very difficult to establish
cd/dvd فیلم آموزشی تکنیک های پیوند زنی درختان
قیمت: ۱۴۰۰۰ تومان (چهارده هزار تومان)
می توانید
جهت دریافت فیلم آموزشی کلیه پیوند زدن درختان
عدد ۱۲ را به شماره ۹۱۹|۶۵|۵۹|۰۹۱۹ پیامک نمایید.
لینک خرید پستی فیلم آموزشی تکنیکهای پیوند زنی درختان
کپی برداری با ذکر منبع مجاز میباشد ” سایت آموزش پیوند درختان ( www.LinkTrees.ir ) ”
۹۱۹|۶۵|۵۹|۰۹۱۹ تماس تلفنی از ساعت ۹ صبح تا ۲۲ شب
linktrees.ads@gmail.com
منتظر نظرات و سوالات شما در مورد مقالات باغبانی – مقاله روشهای پیوند زدن درخت انگور Grafting Grape Vines هستم














سلام مطلب انگلیسی قوی تر در مورد پیوند زدن درختان دارید؟ بهم خبر بدید ممنون
بله نحوه ارسال و قیمت های مقالات انگلیسی پیوند زدن درختان به ایمیل شما فرستاده خواهد شد